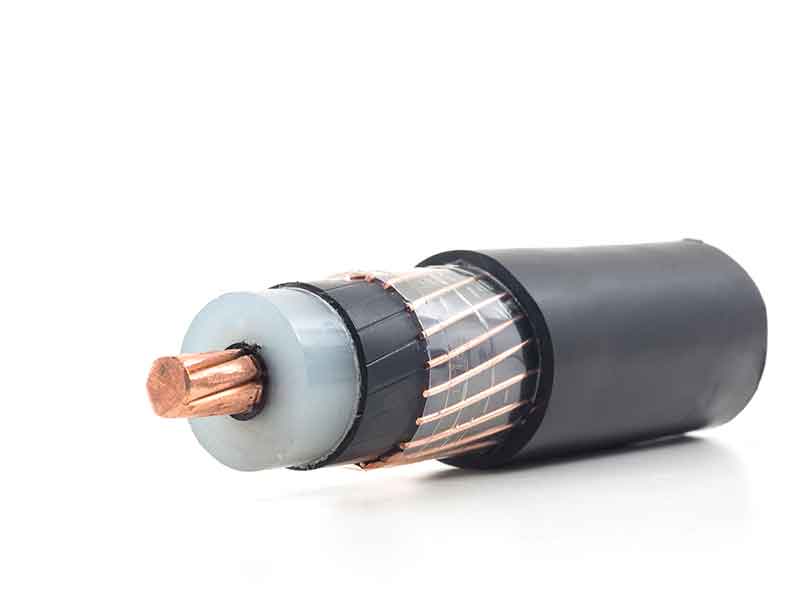
For cables in the medium-voltage (MV) and high-voltage (HV) range, the cable insulation is surrounded by a concentric, semiconductive layer on the inside and outside. These layers serve to homogenize the electrical field in the insulation. The semiconductive layers usually consist of co-polymers based on ethylene, such as EVA, EBA or similar materials, and a high proportion of conductive materials such as soot, graphite or carbon nanotubes, which impart semiconductive properties.
Typical areas of application
Initially, too little importance was attached to the effect of the semiconducting layers on the insulation. However, it was soon realised that the ions contained in the semiconductors can contaminate the intermediate insulation layer and contribute to the formation of water trees.
For the category of strippable MV cables, it is possible to ensure that the outer semiconductor layer can be easily removed from the insulation by selecting suitable polymers and additives, which in certain cases facilitates the assembly of cable fittings in certain cases.
For EPR-based compounds, the ease of removal of the semiconductor remains a basic requirement, as it is difficult to remove mechanically. Volumes are increasing in line with the development and growth of polymeric MV cable insulation.
Benefits
BUSS compounding technology offers the following specific benefits for semi-conductive cable compounds
Compounding requirementsfrom Semicon
The requirements for the compounding process of semi-conductive cable compounds are very demanding. Conductive properties must be ensured at both room temperature and elevated operating temperatures. The structure of the highly structured carbon blacks must be retained and they must be distributed extremely homogeneously to form the conductive network. The polymers used must degrade as little as possible. The surfaces of the layers co-extruded during processing must be very smooth and uniform. In most cases, peroxide-based cross-linking is required.
The BUSS Co-Kneader can fully exploit its specific strengths to meet this complex set of requirements for semiconductive cable compounds: the high proportions of conductive additives can be introduced at several feed points. The immediately initiated mixing processes at moderate shear rates lead to excellent distributive mixing results without damaging the internal structure of the conductive materials and polymers.
The design freedom of the system also makes it possible to specifically address the increasing viscosity in the processing zones with carefully selected configurations. This allows customised control and monitoring of the process conditions.
In the two-stage BUSS Co-Kneader system, the compounding and pressure build-up steps are strictly separated. This means that the compounding step is optimized for the best possible results in terms of quality and throughput, independently of the pressure build-up, filtration and shaping steps.
The modular and therefore adaptable design of the entire compounding system and BUSS's broad-based process expertise make the BUSS Co-kneader the technology leader and system of choice for almost all needs in the compounding of semi-conductive cable compounds worldwide – regardless of the installation location and the required output rate.
Typical plant layout
COMPEO for semi-conductive cable compound production
Take a look at our typical plant layout for semi-conductive cable compounds in our COMPEO showroom.
BUSS Co-Kneaderworldwide
Our patented Co-Kneaders are used worldwide nowadays, supporting our customers in the production of plastics. Using BUSS compounding systems, our customers can master all the demanding requirements for manufacturing semi-conductive cable compounds.
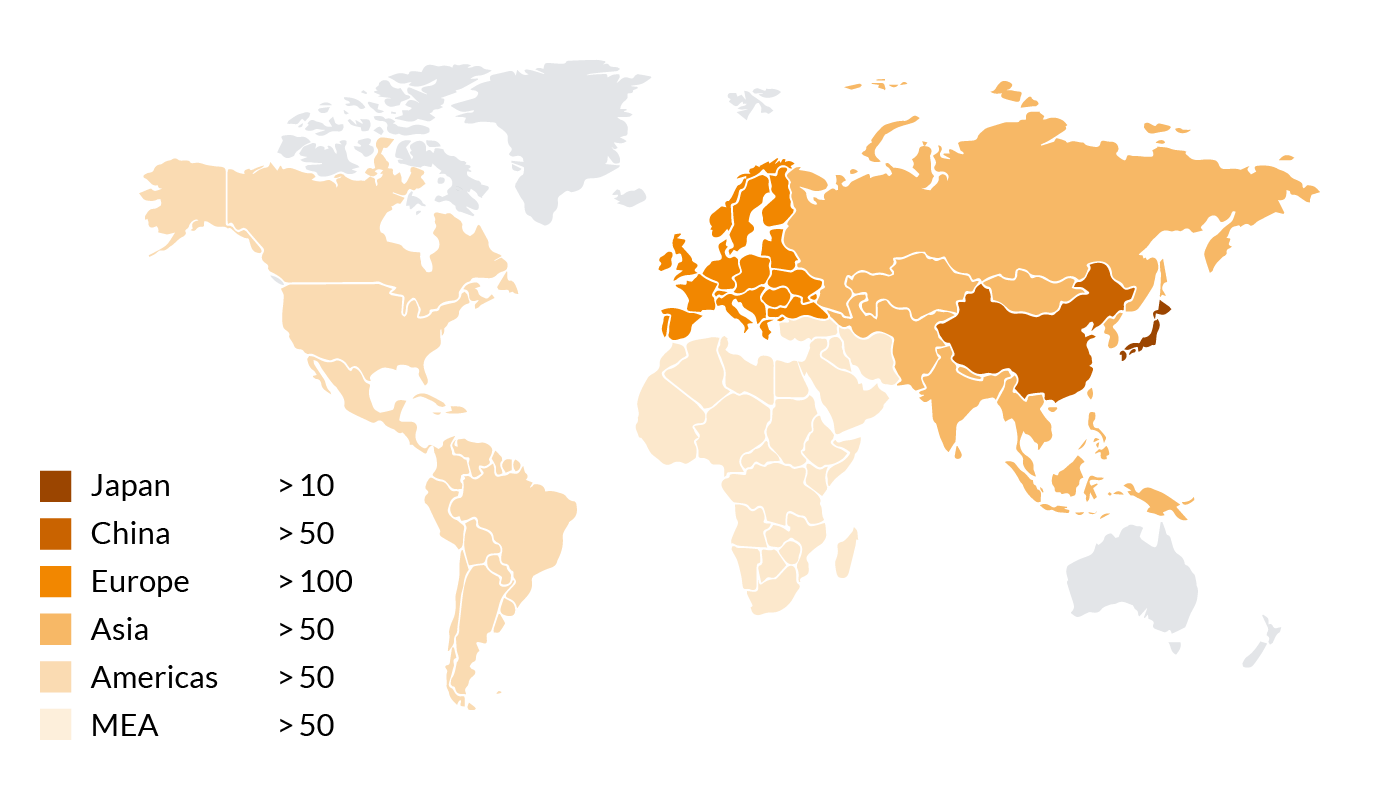
Number of Co-Kneaders used for manufacturing cable compounds