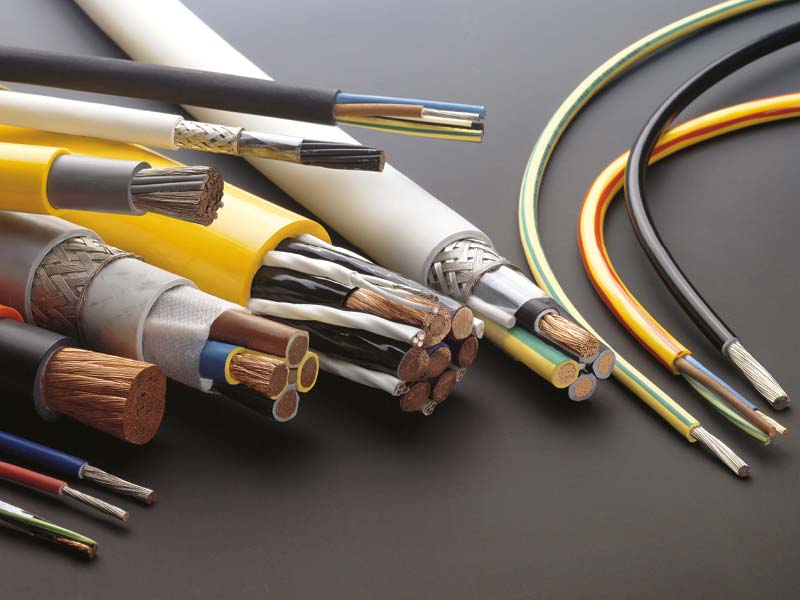
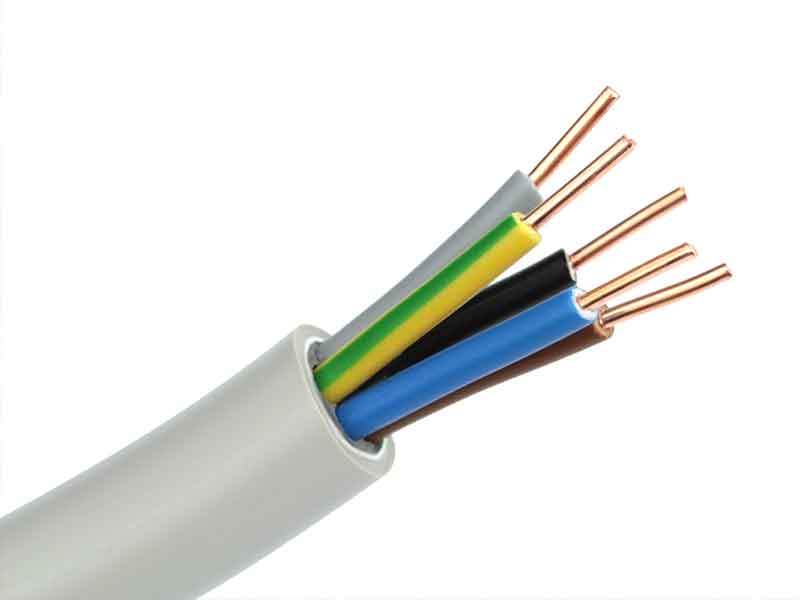
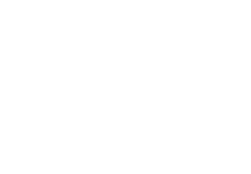Depending on the requirements profile, different plastics are used for manufacturing cable sheathing with BUSS compounding systems. These include polyolefins, TPE, PPE, EEFE, PVA and naturally flexible PVC cable compounds. The use of PVC as cable sheathing has been known since 1932 and was originally used as a substitution product for rubber.
Typical areas of application
Due to the relatively high dielectric resistance, which leads to corresponding losses and heating in the alternating current field, soft PVC compounds are used up to a voltage of 10 kV. They account for the majority of applications in this field. By adjusting the formulations, the application temperature, the mechanical properties such as flexibility in the application, flammability and processing can be customised.
Here are two examples:
- By adjusting the type of plasticiser, the continuous application temperature can be increased up to 105°C.
- With the addition of aluminium trihydroxide, the flame resistance and smoke formation can be improved in a targeted manner. The regulators such as VDE, EN or UL specify standardised property profiles for insulation and sheathing compounds.
The main areas of application are power transmission up to the 10 kV mentioned above, domestic installations, especially in the private sector, and data transfer in general. In the automotive industry, soft PVC cable compounds are used almost exclusively.
Benefits
BUSS compounding technology offers the following specific benefits
Compounding requirementsof PVC cable compounds
The preparation of the PVC cable compounds takes place exclusively in 2 stages: via a hot/cold mixing process in the powder phase with following compounding and pelletizing on the BUSS Co-Kneader.
The compounding requirements can be described as follows: The plasticizer content absorbed in the porous PVC grain and the further formulation components such as stabilizers, additives, fillers and reinforcing agents, flame-retardants, etc. must be specifically gelled, dispersed and distributively mixed and broken down. Well-defined temperature limits must be observed.
The customized property profiles result in wide-scale diversity of formulations with rather decreasing batch sizes which are produced efficiently.
The BUSS Co-Kneader can exploit its performance strengths with uniform, moderate and, if required, adjustable shear rates. The free volumes are designed and realised along the process axis according to the requirements. In most cases, it is possible to produce the entire range using universal shaft geometry designed for the formulation portfolio.
The modularity of the entire system (shaft geometry, installations, shaping options, etc.) also enables adaptation to changing requirements at all times. This provides a top level of investment security.
Low specific energies with the most intense mixing processes, volumetric scale-up processes and the highest availability due to the large operating range emphasize the fact that the BUSS Co-Kneader is and remains first choice for compounding insulation mass from PVC cable compounds.
Typical plant layout
BUSS Co-Kneaderworldwide
Our patented BUSS Co-Kneaders are used worldwide nowadays, supporting our customers in the production of plastics. Using the BUSS compounding systems, our customers can master all the demanding requirements for manufacturing PVC cable compounds.
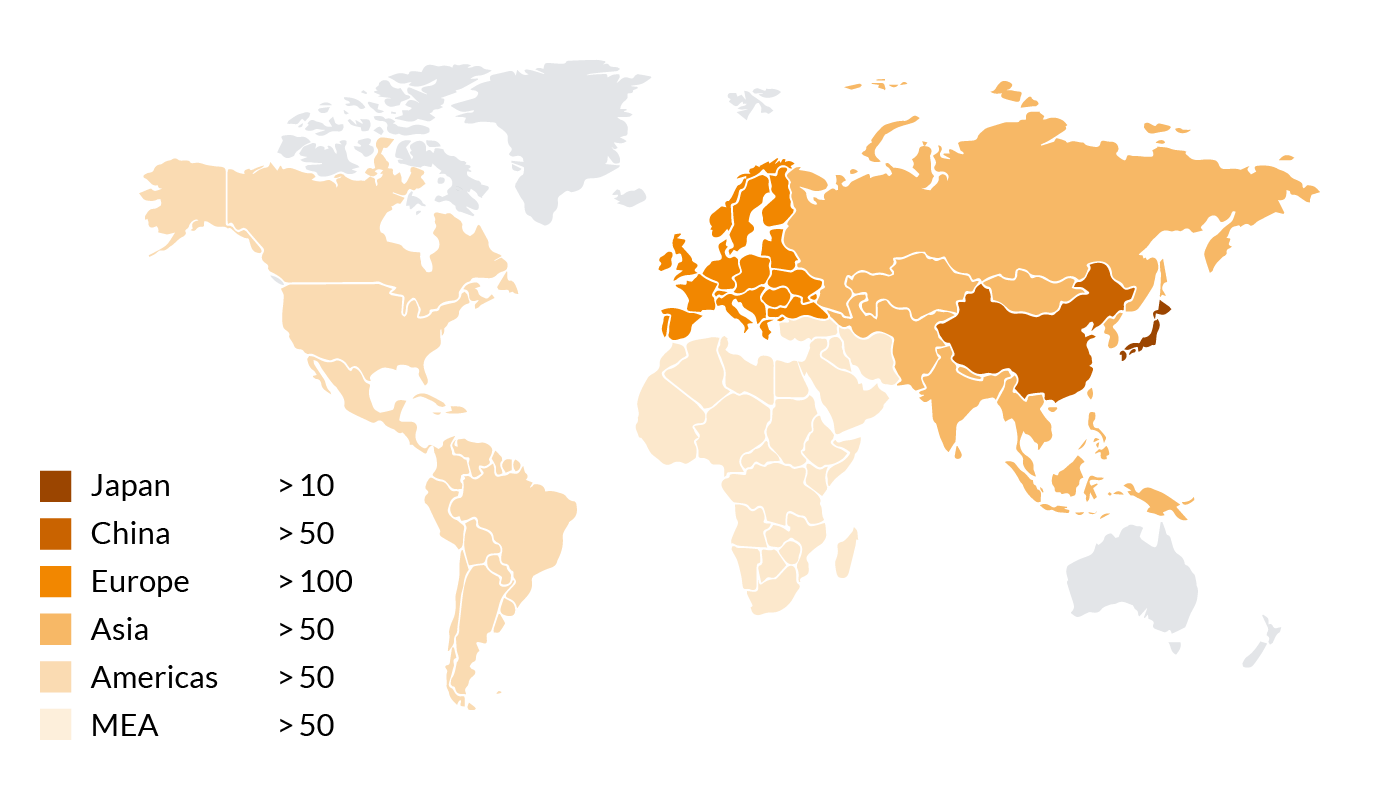
Number of Co-Kneaders used for manufacturing cable compounds