The polycarbonate (PA) compounds belong to the group of technical plastics. The term “engineering plastics” is often used. It basically describes the major strengths and therefore the fields of application: the very good impact strength in a wide continuous temperature operating field in technical parts is highly valued, whilst the excellent transparency enables wide optical and also data carrier applications. In the construction sector, PC is used as opposed to alternative materials due to its good flame resistance properties.
Typical areas of application
Polycarbonate was first described at the end of the 19th century, but only industrially produced since the 1950s by the companies Bayer (now Covestro) and General Electric (now Sabic). Further manufacturers started later.
In addition to the major properties described above, the following properties have become increasingly important: very good electrical insulation capacity, sterilisation capability and compatibility with other plastics such as ABS, ASA or PBT as corresponding customized blends. Therefore, polycarbonate (PC) applications gained considerable significance in electronics/electrotechnology, medical technology and the transport and aircraft industry.
Benefits
BUSS compounding systems offer the following specific benefits
Compounding requirementsof polycarbonate
The compounding system is important for all polycarbonate (PC) materials: the polycarbonate base materials are normally available as powder or in chip form and are converted into granules in the compounding system via a compounding step with the addition of additive components as granulates, for example in the case of transparent molding compounds.
In several cases reinforcement agents, flame retardants, colors or, as mentioned, the blend partners are added. The compounding of these materials is correspondingly demanding and requires customized solutions. Therefore, it is important to melt the polymer components as gently as possible, distribute flame retardants excellently and enter the reinforcement fibers so that the desired mechanical property profiles are achieved.
These demanding requirements are addressed by well thought-out compounding processes and mastered very well.
Compared with alternative compounding systems, the BUSS Co-Kneader can play out its specific strengths very well: the extremely uniform and moderate shear rates generate the lowest possible yellowing because the system does not generate any hotspots. This is crucial for transparent formulations.
The characteristic of the BUSS Co-Kneader to be able to process wide viscosity ranges faultlessly allows very wide and robust operation windows. Therefore, PC blends, reinforced, flame retardant or highly viscous formulations and also their combinations can generally be processed with one shaft geometry.
With the BUSS Co-Kneader's two-stage system, compounding and the pressure build-up steps are strictly decoupled. This enables optimization of the process steps independent of each other. For PC compounds, normally a gear pump is used as a pressure build-up device for granulation. The hinged compounder system and BUSS Co-Kneader housing secures fast access to and high availability of the system.
The modular and therefore adjustable structure of the entire line and the well-established BUSS process expertise make the BUSS Co-Kneader an excellent choice for compounding demanding polycarbonates.
Typical plant layout
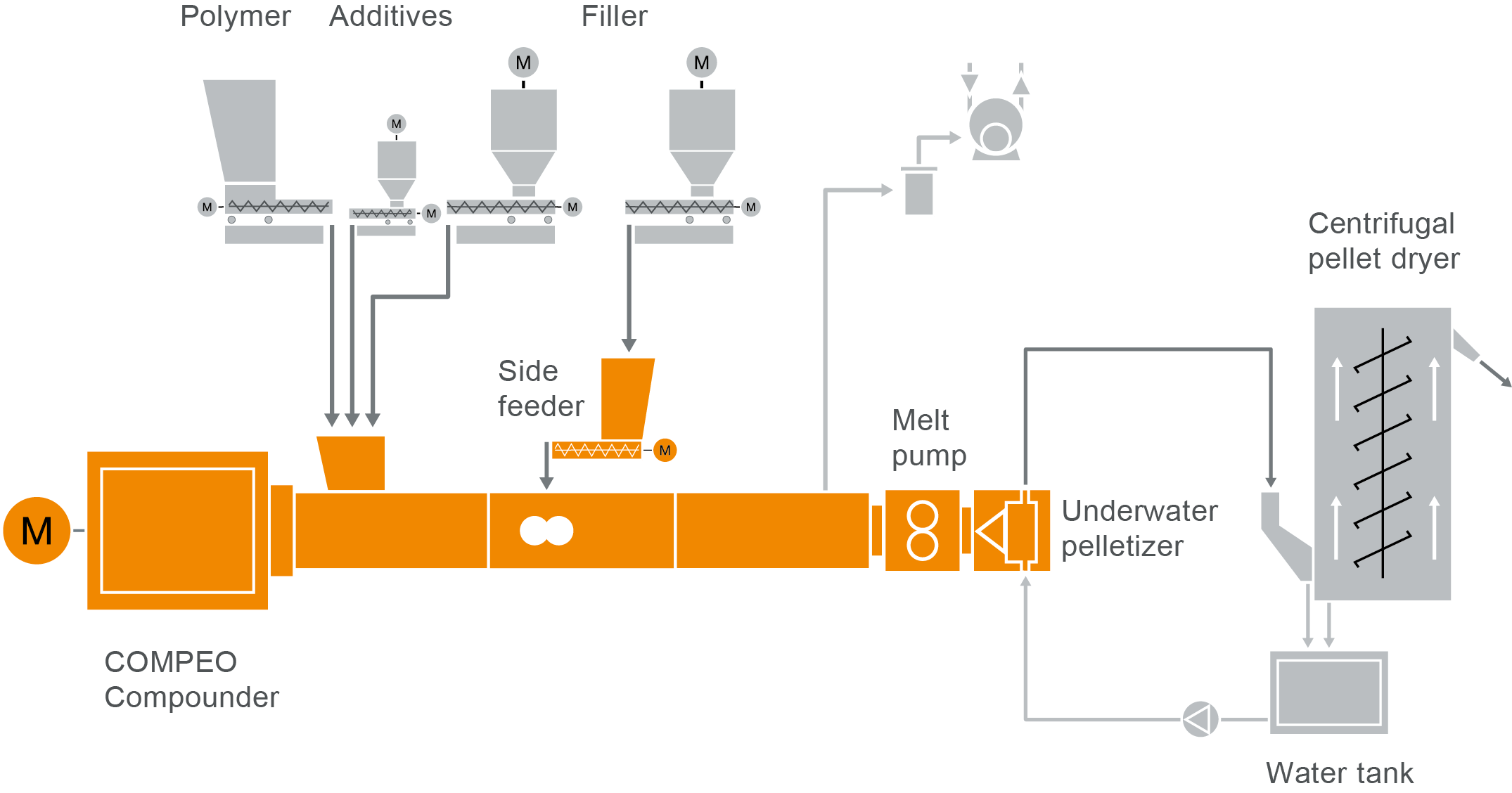
COMPEO compounder for polycarbonate compounding
Take a look at our typical plant layout for the production of polycarbonate compounds and polycarbonate blends in our COMPEO showroom.