Polyisobutylene (PIB) belongs to the olefine polymer family. It has been manufactured commercially since the 1930s and is produced with a wide viscosity range from oil-similar to raw rubber-like masses. Here, its properties largely depend on the average molar masses.
Since the early 1980s, the potential of continuous process management has also been recognized for gum base manufacturing and been used increasingly since then. The constant, reproducible and uniform product quality, short residence times, gentle treatment of sensitive formulation components, precise and fully automated process control, reduced salary costs, low specific energies and therefore reduced energy costs and last but not least reliable and mathematically modelable scale-up processes belong to the major reasons there. BUSS compounding technology is designed for these requirements in the gum base area.
Typical areas of application
In addition to the technical applications which are described on the corresponding pages, PIB is often used as an elastomer formulation component in the basic mass for chewing gum, the so-called gum base. As opposed to the natural rubber originally used, the individual requirements profiles of the type, brand and manufacturer-specific features can be mapped very well with the wide range of different PIB variants and together with the further formulation components.
Benefits
BUSS compounding systems offer the following specific benefits
Compounding requirementsfor gum base
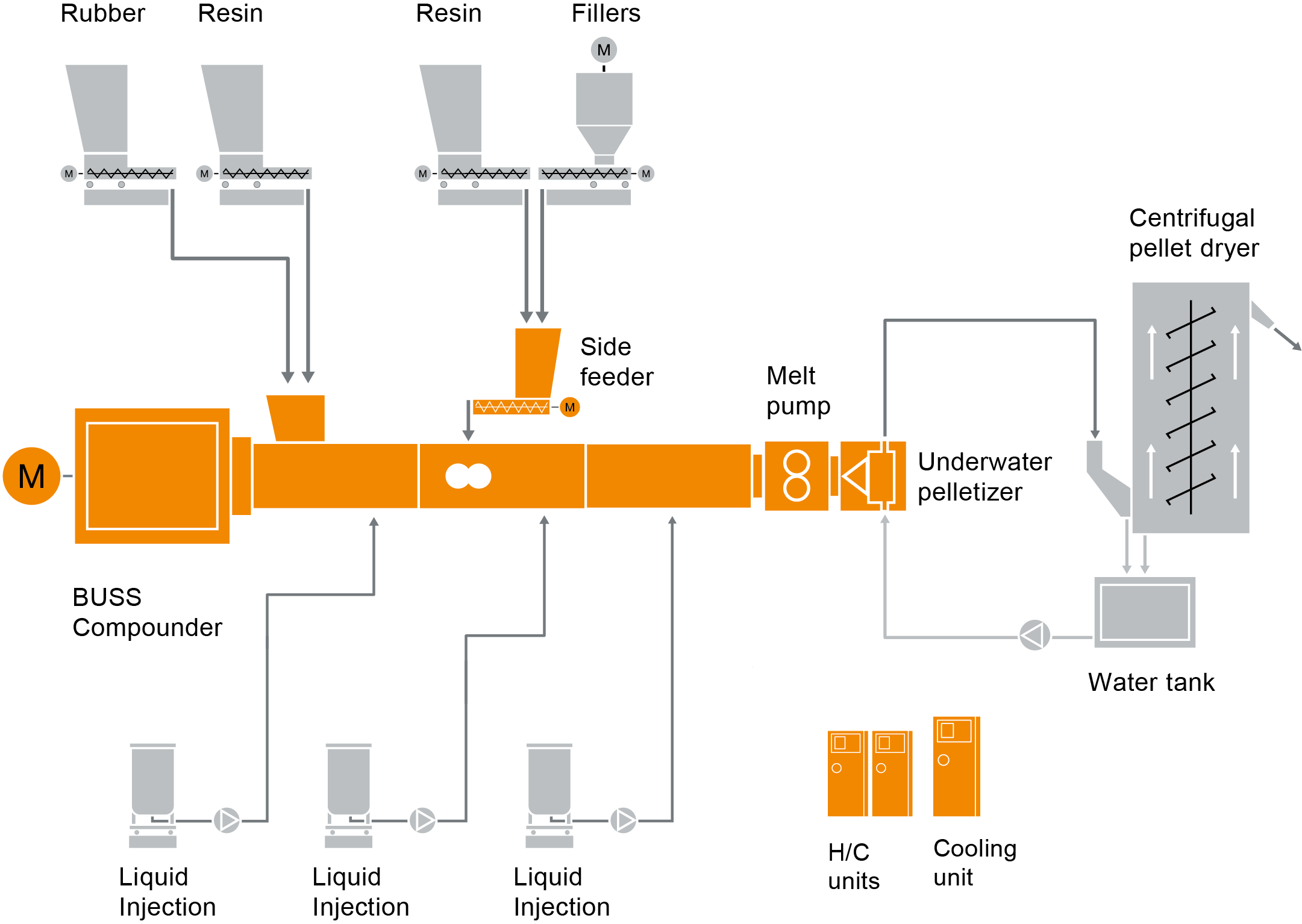
In the compounding process for gum base, it is important to mix the formulation components optimally in the viscous phase. BUSS compounding technology is ideally suitable for this. The elastomers (PIB) and also the liquid rubber shares are melted or masticated via the dissipated kneader shaft shear energy in the first zone of the BUSS Kneader.
In the second zone, the fillers and epoxies are dosed additionally and mixed in. The synchronised course of dissipative and distributive mixing processes via the oscillating and rotating screw shaft is particularly effective here. The waxes, plasticizers and antioxidants, which often exist as liquids, are fed to the optimal process position via hollow-drilled kneading pins.
In the third zone, in addition to further homogenisation of the gum based, reworking material can also be integrated. Thus, it is possible with a process length of only 11 L/D to process the product gently with first-class product quality at high throughput. Due to the short dwell time and excellent self-cleaning properties, it is possible to work with on-the-fly product changes, thus optimizing availability.
The mass thus prepared can then be further processed inline. For this purpose, it is normally pumped into a heated intermediate storage container. Alternatively, shaping takes place for further processing offline.
This can be a granulation (e.g. hot cutting) or pelletizing (e.g. Rotoform) process or also classical molding of slabs using sausage-shaped gum base extrudates lying next to each other. Thanks to its technologically outstanding features and highly efficient operating system, the BUSS Kneader has become the reference for compounding technology for gum base processing. Our numerous customers are well aware of the excellent options and therefore opted for a BUSS Kneader technology several decades ago.
Typical plant layout