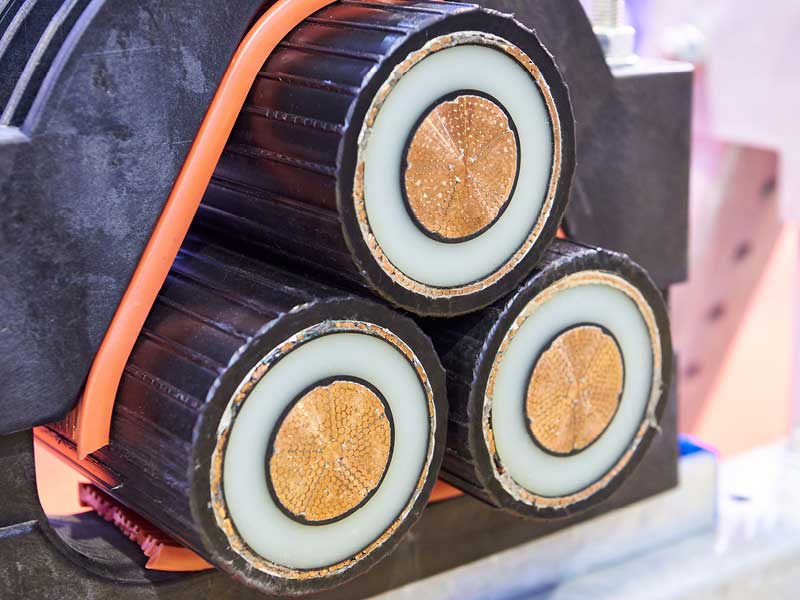
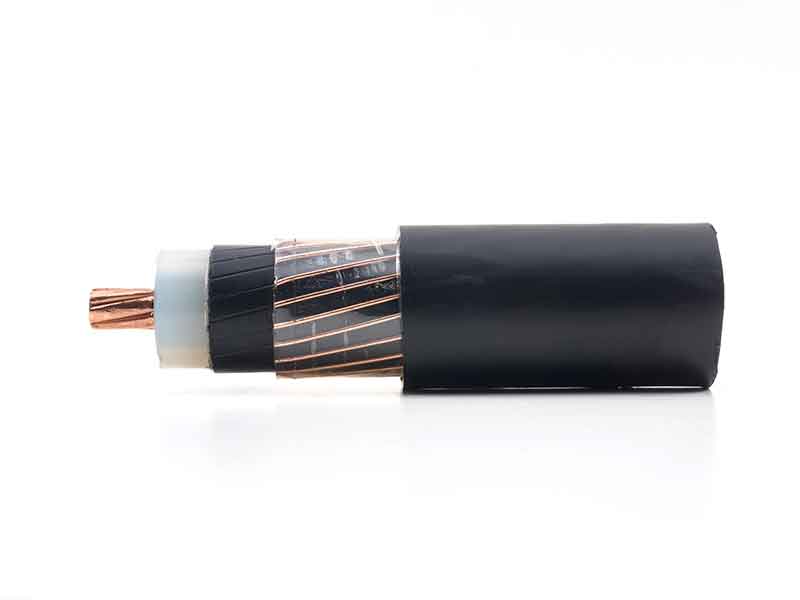
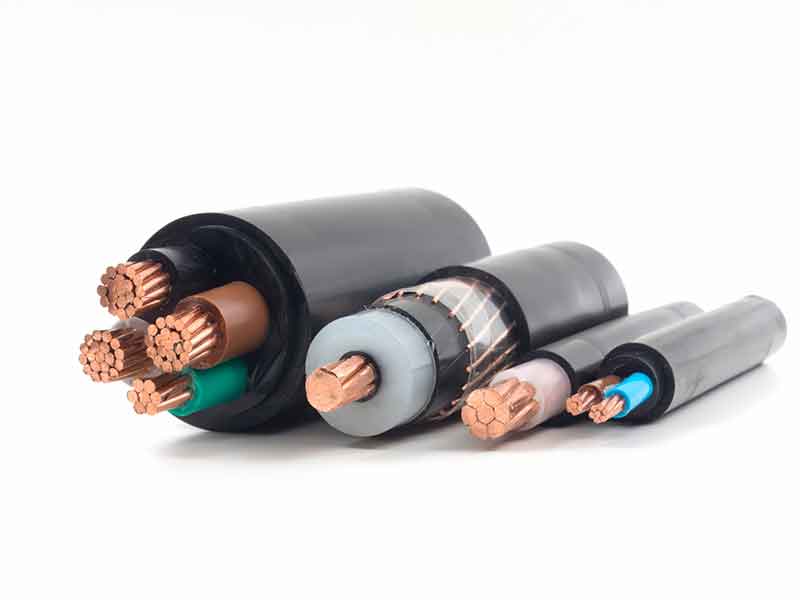
Polyethylenes (PE) demonstrate excellent insulation properties. A temporary increase in temperature, e.g. due to a load peak in the application as cable insulation can, however, cause full functional failure: the relatively low softening or melting ranges cause thermomechanical failure or even dripping off the insulation.
By crosslinking the polyethylene (PEX or XLPE stands for cross-linked PE), a thermoset material can be made from the thermoplastic material.
This can be used at considerably higher operating temperatures, has better mechanical properties, is more stable against organic fluids and often allows thinner wall thicknesses. Various crosslinking methods are used for manufacturing XLPE compounds for cable insulation.
Typical areas of application
The XLPE cable compounds are also described as PEX-a. The manufacturing process for peroxide cross-linked polyethylene was patented during the 1960s and has been used since then in the cable industry. In an initial step, basic polymer, peroxide and additives are mixed intensely whilst adhering to process temperatures not exceeding 130°C.
The crosslinking process takes place under pressure and temperature on a so-called CV (continuous vulcanisation) line directly after processing. Due to the relatively work-intense process, this technology is primarily used for high-performance cables.
The development of water tree resistant formulations and processes made XLPE cable compounds increasingly the material of choice for mid-voltage (MV) and high-voltage (HV) insulation for alternating current applications. For high-voltage use in the direct current area, they are the preferred material selection. For urban energy supply, more and more overhead lines are being replaced with underground cables or these are laid from the outset.
The connection of offshore wind farms to the grid, and sea cables in general is very frequently realised with cable insulation consisting of XLPE compounds. For these markets, which follow global megatrends, we can continue to calculate with huge mass volumes and growth. And BUSS compounding systems are the perfect partner for manufacturing the basis of this cable insulation, XLPE cable compounds.
Benefits
BUSS compounding systems for XLPE compounds offer the following specific benefits
Compounding requirementsof XLPE
The applications require the intense mixing of the formulation components with strict process management regarding the temperature profile and degree of purity of product and plant. For MV- applications, the peroxide is injected directly into the polymer melt and mixed intensively at low temperatures. The compound is filtered and granulated.
For HV applications, the plant design and its operation are focused on absolute purity: the basic polymers are pre-filtered, contamination sources within and outside the plant are eliminated and production takes place in cleanroom atmosphere.
The following properties of the BUSS Co-Kneader and of the entire compounding system for XLPE cable compounds are the success factors for this process: the peroxide is injected directly into the process zone and distributed optimally thanks to the immediately effective distributive mixing. The moderate and uniform shear rates ensure that this takes place at low process temperatures and with minimized polymer degradation. The cascade line structure also allows gentle melt filtration and pelletizing.
The complete compounding systems realised exemplify the fusion of BUSS process engineering, mechanical engineering and plant construction expertise as a reference for this industry.
Typical plant layout
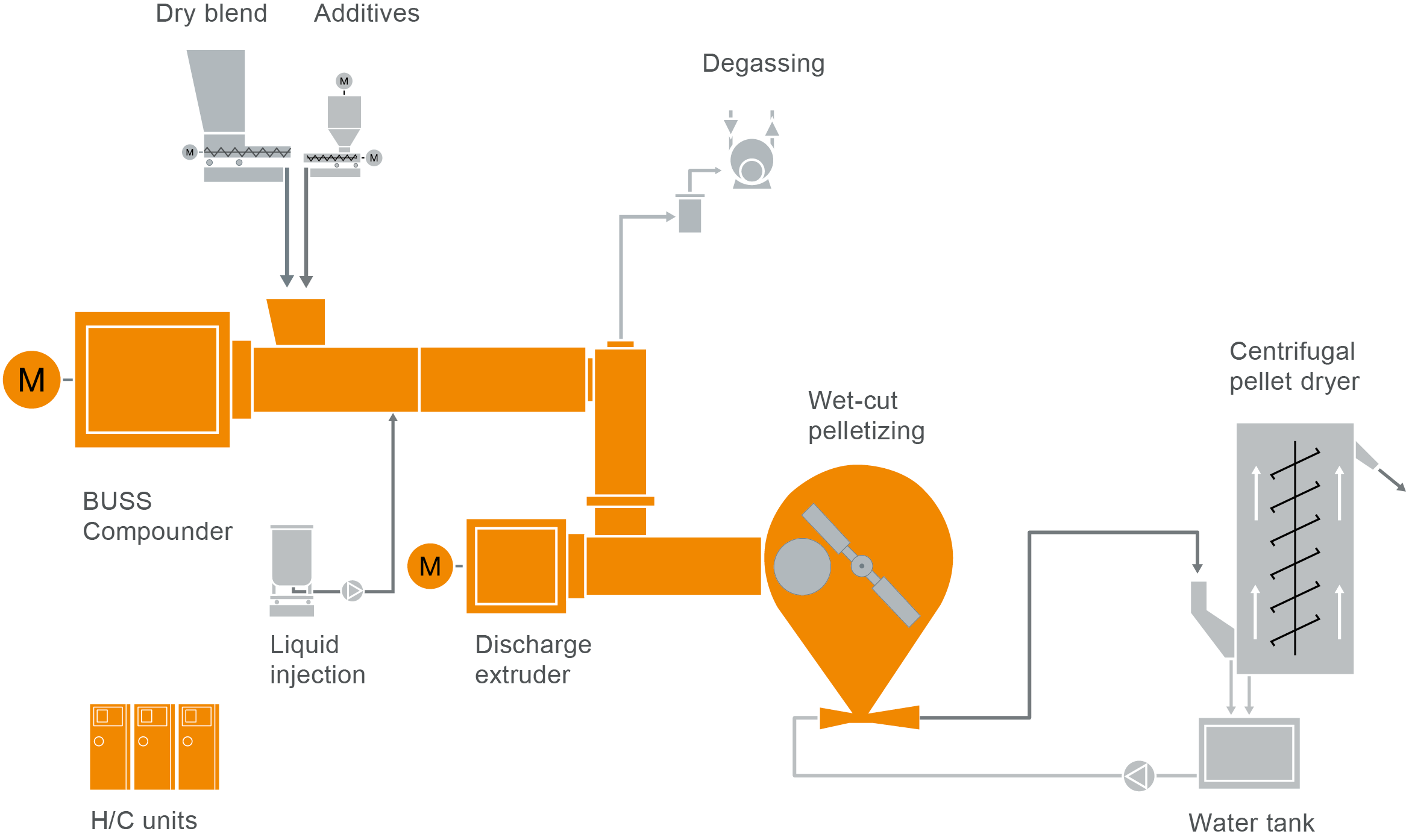
COMPEO cascade layout for manufacturing XLPE cable compounds
Take a look at our typical plant layout for the production of XLPE compounds in our COMPEO showroom.
BUSS Co-Kneaderworldwide
Our patented BUSS Co-Kneaders are supporting our customers in plastics production of plastics worldwide nowadays. With BUSS compounding systems, our customers can master all the demanding requirements for manufacturing XLPE cable compounds.
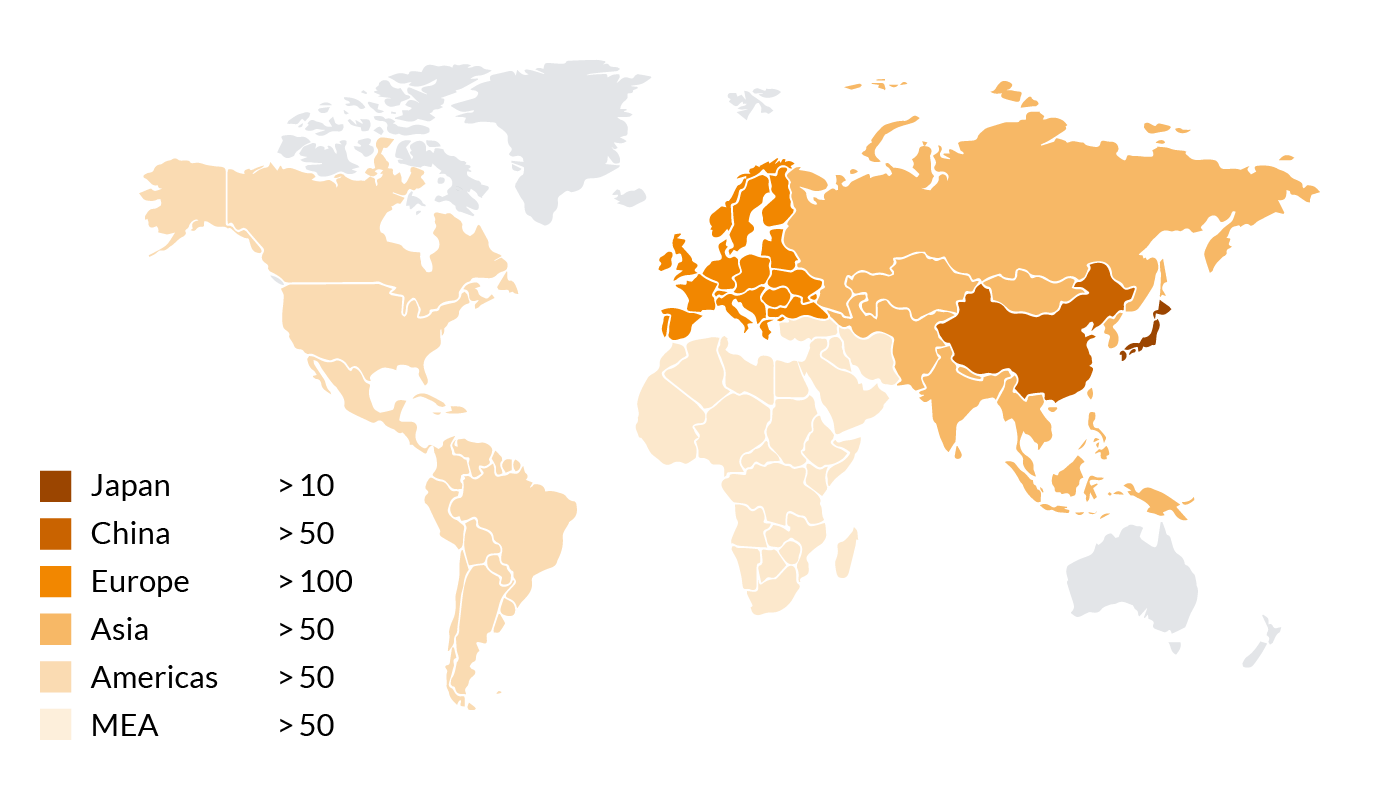
Number of Co-Kneaders used in the cable industry