The polymers PET and PBT belong to the polyester family. PBT stands for polybutylene terephthalate, PET for polyethylene terephthalate. PET can both exist as amorphous molding material (PET A) and as partially crystalline material (PET C). PBT is considered to be partially crystalline.
They are both thermoplastic and manufactured using polycondensation. They belong to the group of technical plastics. The term “engineering plastics” is also used frequently. It describes its basic major strengths and therefore its fields of application: technical components with demanding mechanical, thermal, and electrical performance requirement profiles and chemical durability.
PET / PBT were originally manufactured in larger quantities in England in the 1940s. Their original use in textiles and materials of all kinds was extended to injection molding and extrusion applications.
Typical areas of application
Due to its faster crystallisation, PBT is mostly used for injection molding applications. The balanced combination of stiffness and firmness with good viscosity and heat resistance as well as dimensional stability, also in challenging surroundings, make PBT compounds an important material in electronics/electrotechnology, the car and aircraft industry and others.
The major use of PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is bottles (85%), APET (amorphous polyethylene terephthalate, 7%) and CPET (crystalline polyethylene terephthalate, 8%). The compounding step plays an important role for the specialities.
Individual property profiles are achieved with reinforcing agents, fillers and flame retardants. The individual property profiles are achieved with further additives as well as elastomer modifications. Here, it is above-all important to take account of temperature and shear sensitivity in the compounding technology for PBT (polyethylene terephthalate). Both PET and PBT are also used as blend partners for customized compounds.
Benefits
BUSS compounding systems offer the following specific benefits
Compounding requirementsfor PBT / PET compounds
The compounding is correspondingly challenging. Therefore, it is important to melt the polymer shares and, if applicable, the blend shares gently and without shear peaks homogeneously and to distribute the shares of filling agents and flame retardant agents excellently. This is highly demanding in compounding technology. The reinforcement fibers must be inserted in a manner which achieves maximum physical properties and that the service life remains high in the respective process zones.
These requirements which partially contradict each other are mastered well, using sophisticated processes. The BUSS Co-Kneader has proven itself over a long period when compounding these demanding materials.
The moderate and uniform, if necessary also specifically adaptable, shear rates and with them precise temperature management of the BUSS Co-Kneader play the central role here: in the melting zone only as much energy as required is dissipated without overburdening the polymer components.
The filling and flame retardant agents are distributed optimally within the shortest process section due to the high folding values, reinforcement fibers are added, separated and then wrapped if necessary in order to maintain the maximum fiber lengths.
Important market players rely exclusively on the specific advantages offered by the BUSS Co-Kneader technology in this field. With the two-stage BUSS Co-Kneader system, compounding and the pressure build-up steps are strictly decoupled. This enables independent optimisation of the process steps. The modular and therefore adaptable line structure and the widely supported BUSS process expertise around the PBT and PET compounding technology make the BUSS Co-Kneader a very good choice for compounding the wide range of PET and PBT compounds.
Typical plant layout
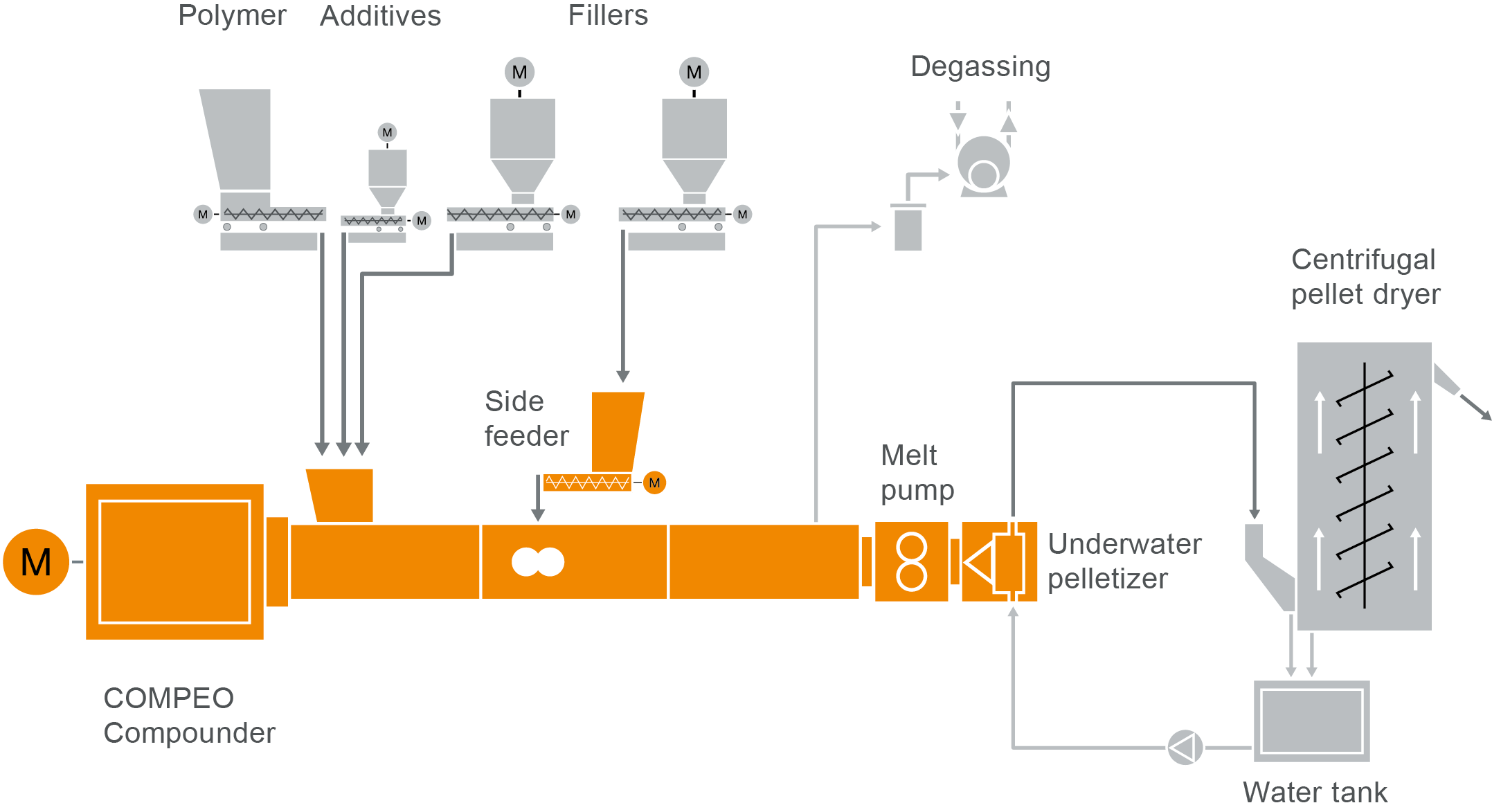
COMPEO compounder for PBT/PET processing
Take a look at our typical plant layout for the production of PBT/PET compounds in our COMPEO showroom.