There are basically two reasons for working fillers into a plastic matrix: to optimize the compound material properties, such as for breathable foils or sound-absorbing pipes, or to save costs.
Typical areas of application
Three variables play key roles in the interaction between fillers and polymer matrix.
- Particle shape: a low aspect ratio such as glass beads, CaCO3 or BaSO4 generally improves the elasticity module, while a large aspect ratio, such as talcum or wollastonite, tend to improve tensile and tear strength as well as the modulus of elasticity.
- Particle size distribution affects how well the fillers are worked in. Important here are the Van-der-Waals cohesion forces between particles (at particle sizes > 1 μm), and the dispersive shear forces exerted by the BUSS Co-Kneader (at particle diameter < 10 μm) for the FRTP compounding systems.
- Surface area of the filler: the number of potential cohesion points between fillers and polymer chains depends on the specific surface area (m²/g), of the fillers. The larger the fillers’ surface area , the more cohesion points and the stronger the material (rigidity, tensile strength, tear and impact strength).
Surface coatings are another important aspect. They can for example influence agglomerate formation, material flowability for easier handling, and adequate wetting during compounding.
Benefits
BUSS compounding systems offer the following specific benefits for FRTP compounds
Compounding requirementsof fiber-reinforced plastics
BUSS process expertise is the key to manufacturing fiber-reinforced plastics: in addition to optimal distribution of the material flows, it is particularly important to have command of the air and humidity flows accompanying filler input.
Consequently, the process geometry must be optimally configured for these tasks. With corresponding configuration, the large free volumes and their corresponding torques allow the efficient production of these fiber-reinforced plastics.
The excellent all-rounder qualities of the BUSS Co-Kneader with its extremely wide operation window enable mostly highly varied related processes including fillers such as talcum, titanium dioxide or barium sulfate as well as aluminium or magnesium hydroxides.
The considerably lower wear and tear compared to alternative screw extruders denotes a positive side-effect of the BUSS Co-Kneader’s moderate shear rates. The modular and therefore adjustable design of the entire compounding system make the BUSS Co-Kneader an excellent choice for compounding filled thermoplastics.
Typical plant layout
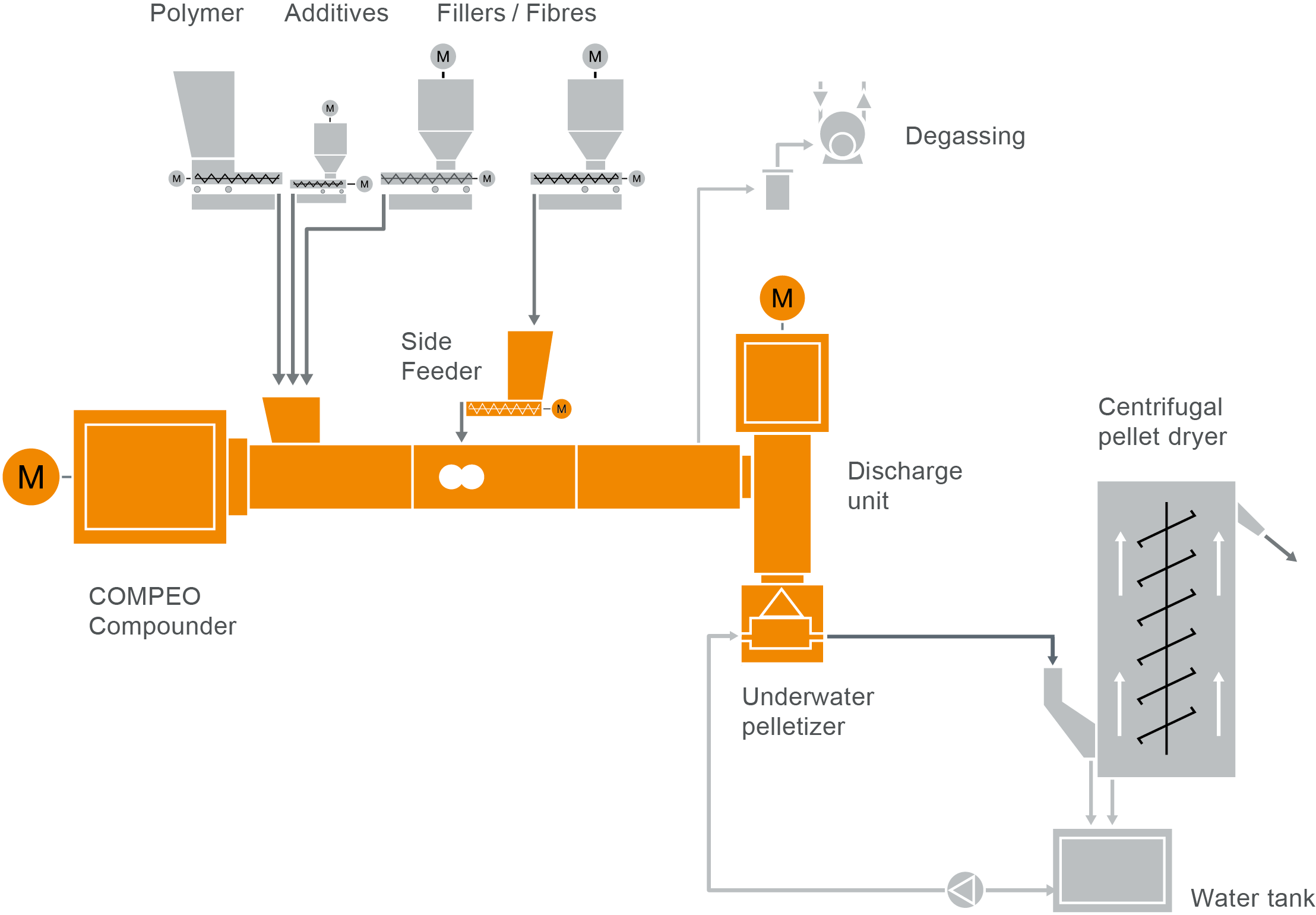
COMPEO compounder for FRTP compounding
Take a look at our typical plant layout for the production of filled and reinforced plastics in our COMPEO showroom.
BUSS Co-Kneaderworldwide
Our patented BUSS Co-Kneaders are used worldwide nowadays, supporting our customers in plastics production. Using BUSS compounding systems, our customers can master all the demanding requirements for FRTP compounding.
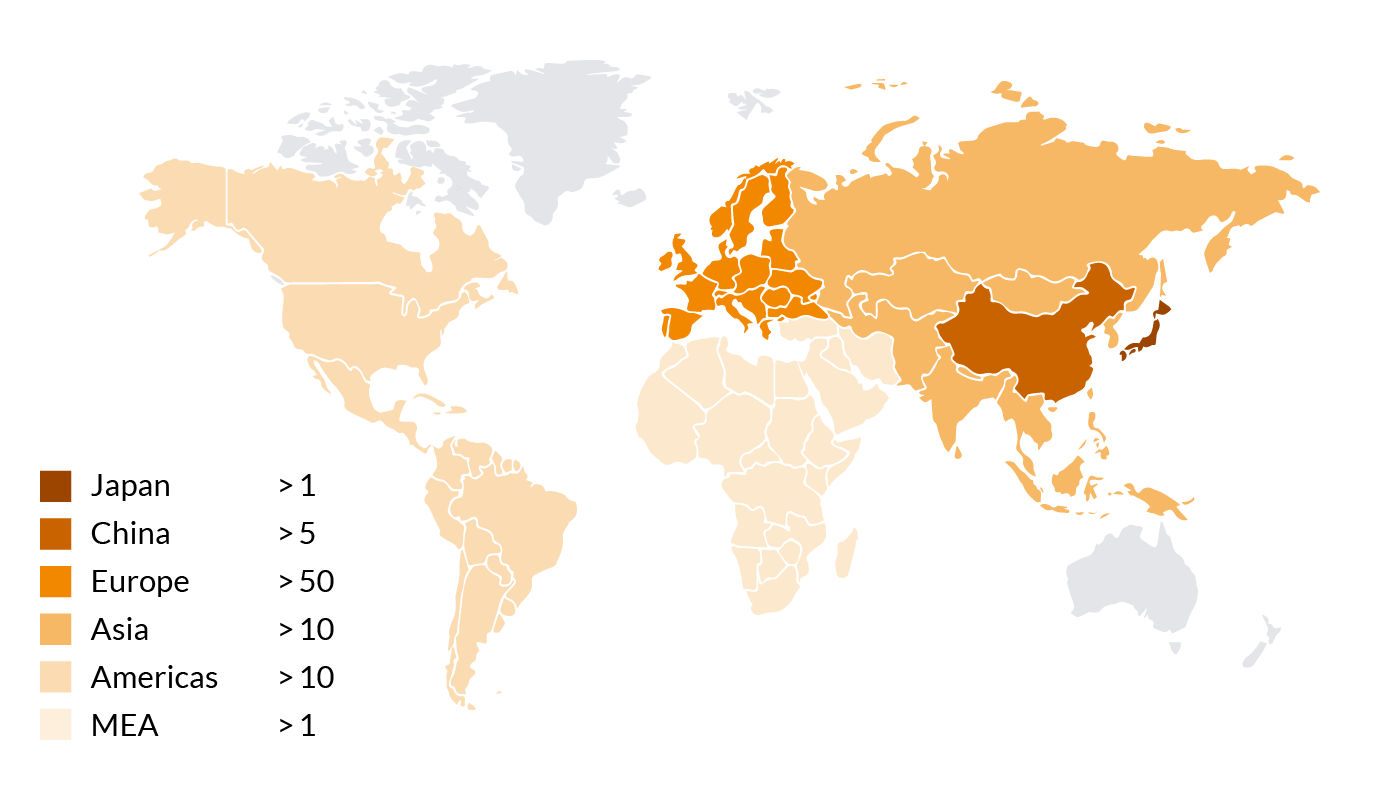
Number of Co-Kneaders used for manufacturing performance compounds